on
스프링 부트 활용 : 테스트
스프링 부트 활용
테스트
프로젝트를 할 때 항상 코드를 작성하는데 있어서 TDD가 강조된다. TDD란 Test-Driven Development(테스트 주도 개발)의 약자로, “테스트가 개발을 이끌어 나간다”고 정의할 수 있다. 스프링 부트에서는 테스트 코드를 작성하기 편리한 기능들이 많이 제공되고 있으므로, 예제를 보면서 알아보자.
우선 스프링 부트에서 테스트 환경을 구성하기 위해서 spring-boot-starter-test 의존성을 추가한다. 프로젝트를 생성할 때 기본적으로 추가를 해주기는 하지만 간혹 없는 경우도 있으니 의존성을 확인하도록 하자.
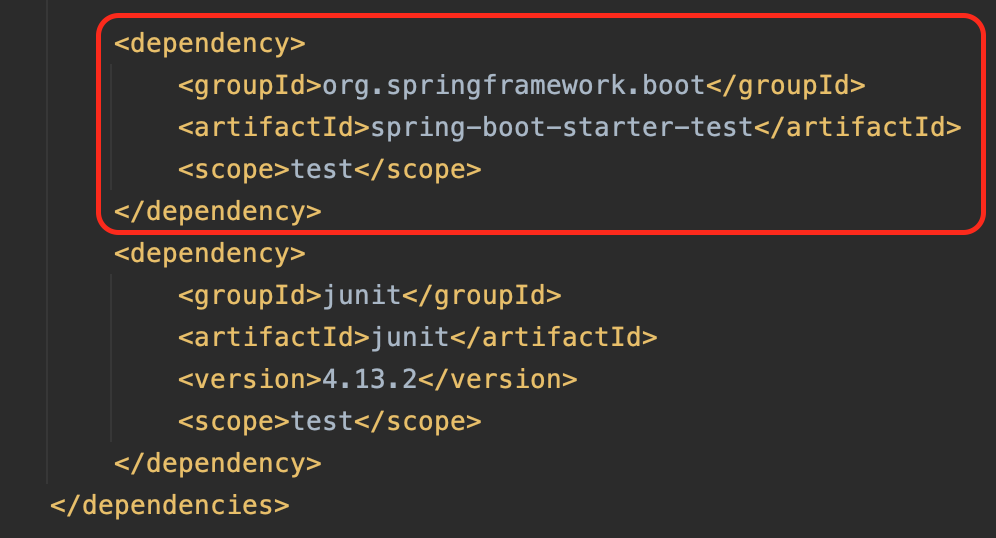
테스트 예제
Controller를 하나 만들어서 Service를 호출한 뒤 /hello라는 요청을 보내면 hello + [text]가 출력되는 예제를 만들어 보자.
먼저, SampleController와 SampleService를 만든다.
▶ SampleController.java
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class SampleController {
@Autowired
private SampleService sampleService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello " + sampleService.getName();
}
}
▶ SampleService.java
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class SampleService {
public String getName() {
return "grace";
}
}
이제 Controller 클래스가 잘 동작하는지 확인하기 위해서 테스트해보고 싶다. SampleControllerTest 파일을 만들자. test 디렉토리 아래에 직접 만들어도 되고 SampleController 클래스에서 Command + N를 눌러서 만들어도 된다. 인텔리제이의 경우 Command + Shift + T로 만들 수 있다.
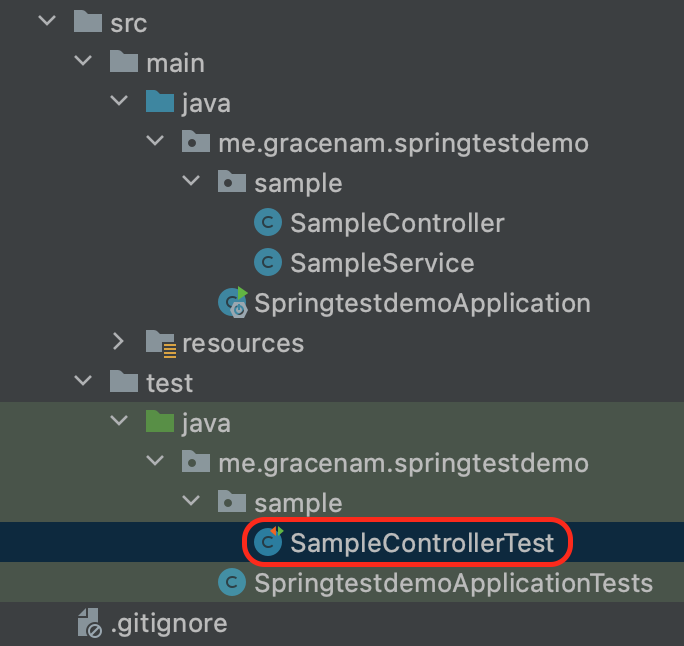
Test를 실행하기 위해서는 spring-boot-starter-test 의존성이 필요하기 때문에 꼭 확인하도록 하자.
▶ SampleControllerTest.java
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultHandlers.print;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class SampleControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string("hello grace"))
.andDo(print());
}
}
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)와 @SpringBootTest, 이 두 애노테이션이 붙어있는 것이 테스트 코드의 가장 기본적인 형태이다. 이 코드를 보고 ‘빈 설정 파일은 설정을 안해주는 것인가?’라는 의문이 생길 수 있다. 이 부분은 걱정할 필요가 없는데 @SpringBootApplication에서 알아서 찾아주기 때문이다.
...
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.MOCK)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class SampleControllerTest {
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
...
@RunWith는 JUnit의 테스트 러너를 확장하는 방법 중 하나로 커스텀 테스트 러너를 설정해주는 방법이다. 테스트를 진행할 때 JUnit에 내장된 실행자 외에 다른 실행자를 실행시킨다. 위 코드에서는 SpringRunner.class를 설정했기 때문에 SpringRunner라는 스프링 실행자를 사용한다. 이처럼 @RunWith는 스프링 부트 테스트와 JUnit 사이에서 연결자 역할을 한다.
💡 JUnit5 부터는 @RunWith을 사용하지 않는데 그 이유에 대해서는 기선님이 작성하신 스프링 부트, @RunWith가 더 이상 보이지 않는 이유를 참고하자.
@SpringBootTest는 @RunWith과 함께 사용해야한다. 이 애노테이션에는 webEnvironment라는 속성이 있는데 이 속성의 기본 값은 MOCK으로 되어있다. 속성의 값은 다음과 같다.
- MOCK : mock servlet environment. 내장 톰캣을 사용하지 않음.
- RANDOM_PORT / DEFINED_PORT : 내장 톰캣을 사용함.
- NONE: 서블릿 환경을 제공하지 않음.
여기서 사용하는 Mock에 대해서 조금 더 알아보자.
Mock 타입 테스트
Mock 타입은 Servlet Container(톰캣, jetty 등등)를 테스트용으로 띄우지 않고, Mockup1을 해서 Servlet을 Mocking2한 것을 띄워준다. dispatcherServlet이 생성은 되지만 Mockup이 되기 때문에, dispatcherServlet에 요청을 보낸 것‘처럼’ 테스트를 할 수 있다. 이 때 mockup 된 Servlet과 상호작용을 하려면 MockMVC라는 클라이언트를 사용해야 한다.
MockMVC라는 클라이언트를 사용하려면 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 애노테이션을 추가하고 @Autowired를 사용해서 주입받는 방법이 가장 쉽다. 이 외에도 여러가지 방법이 있는데 스프링 부트 최신 버전에서 MockMVC를 만드는 방법은 애노테이션을 추가하는 것이 가장 쉽다.
이제 테스트를 작성하면 된다.
...
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(content().string("hello grace"))
.andDo(print());
}
}
테스트하고 싶은 메소드에 @Test를 붙이면 해당 메소드를 테스트 대상으로 지정할 수 있다.
perform() 메소드는 입력된 값을 수행하는 메소드로 여기서는 MockMvc.perform(get())의 형태로 작성하였는데 해석하면 MockMvc(MockMvc.)에 요청(get)을 보내는 것(perform)이다. 이 때 에러가 발생할 수 있기 때문에 throws Exception을 추가한다.
andExpect()는 예상 값을 검증하는 메소드로 status().isOk()인지를 검증하는 것이다. status().isOk()는 status의 코드가 200, 정상인지 확인하는 것이다. 이어서 content().string()은 출력되는 결과 값이 expectedContent, 여기서는 “hello grace”라고 주어진 값과 동일한지 확인하는 것이다.
마지막으로 andDo()는 요청에 대한 처리를 해주는 메소드다. 일반적으로 print() 메소드가 들어온다.
이 외에도 어떤 Controller를 썼는지, 어떤 Controller의 어떤 method를 호출했는지, 이 요청이 이 Controller에 제대로 맵핑이 되었는지 등의 다른 옵션들도 존재한다.
정상적으로 테스트 코드를 작성했다면 테스트 코드 실행 시 아래와 같이 출력되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
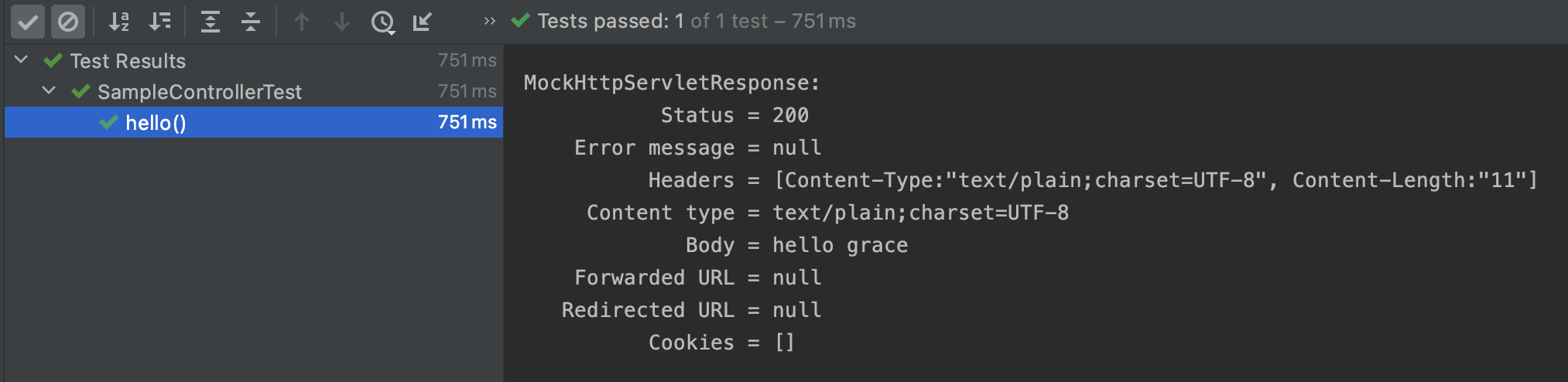
RANDOM_PORT / DEFINED_PORT 타입 테스트
RANDOM_PORT를 사용하면 실제 Servlet Containter인 내장 톰캣이 뜬다. 이 때부터는 MockMvc가 아니라 테스트용 REST template이나, 테스트용 web Client를 사용해야 한다.
▶ RestTemplate
RestTemplate을 먼저 살펴보자. MockMvc 대신 TestRestTemplate을 주입받는다.
...
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class SampleControllerTest {
@Autowired
TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
String result = testRestTemplate.getForObject("/hello", String.class);
assertThat(result).isEqualTo("hello grace");
}
}
테스트 코드를 작성한다. url을 주고(/hello), 원하는 바디 타입을 준 다음(String.class), 이 값을 assertThat으로 확인한다.
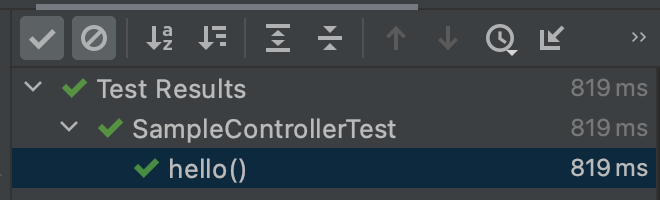
이렇게 할 경우 SampleService단 까지 가기 때문에 테스트가 다소 길어진다. 만약 SampleController까지만 테스트 하고 싶을 때는 어떻게 할까?
@MockBean
@MockBean이라는 애노테이션이 있다. 이 애노테이션을 사용하면 application context 안에 들어있는 빈을 MockBean으로 교체한다.
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class SampleControllerTest {
@Autowired
TestRestTemplate testRestTemplate;
@MockBean
SampleService mockSampleService;
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
when(mockSampleService.getName()).thenReturn("gracenam");
String result = testRestTemplate.getForObject("/hello", String.class);
assertThat(result).isEqualTo("hello gracenam");
}
}
여기서는 SampleController까지만 돌리기 위해서 SampleService를 받아왔다. 이렇게 하면 application context 안에 있는 SampleService bean이 mockbean으로 교체된다. 따라서 SampleService는 mockSampleService를 사용하게 된다.
기존 SampleService에서는 grace를 리턴해줬지만, mockSampleService에서는 gracenam을 리턴하도록 했다. 따라서 출력되는 값은 hello gracenam이 되므로 비교 값을 변경했다.
▶ WebTestClient
WebClient는 SpringMVC Webflux쪽에 추가된 Rest Client 중 하나이다. 우리가 기존에 사용하던 Rest client는 synchronous(동기)하다. 즉, 요청 하나를 보내고 그 요청이 끝날 때까지 기다린 다음 요청을 보낼 수 있다.
반면에 Web client는 asynchronous(비동기)하다. 요청을 보내고 기다리는 것이 아니라 응답이 오면 call back이 event로 오기 때문에, 그 때 call back을 실행할 수 있다.
테스트 코드에서 WebTestClient를 사용해서 WebClient와 비슷한 API를 사용할 수 있다.
WebClient를 사용하려면 Spring Webflux쪽 dependency가 들어와 있어야 한다.
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.reactive.server.WebTestClient;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
class SampleControllerTest {
@Autowired
WebTestClient webTestClient;
@MockBean
SampleService mockSampleService;
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
when(mockSampleService.getName()).thenReturn("gracenam");
}
}
의존성이 주입되지 않은 상태에서 위 코드를 실행하면 당연히 에러가 발생하게 된다. WebClient를 사용하기 위해서 아래의 의존성을 주입해주자.
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
이제 테스트 코드를 작성하자. 작성하는 코드는 Mock 타입 테스트 코드를 작성할 때와 비슷하다.
...
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
when(mockSampleService.getName()).thenReturn("gracenam");
webTestClient.get().uri("/hello").exchange()
.expectStatus().isOk()
.expectBody(String.class).isEqualTo("hello gracenam");
}
}
슬라이스 테스트 Slice Test
지금까지 해온 테스트들은 모두 통합 테스트이다. @SpringBootTest 애노테이션이 @SpringBootApplication 애노테이션을 찾아가서 이 애노테이션부터 시작하는 모든 빈을 스캔하는 것이다. 그리고 스캔한 모든 빈을 테스트용 애플리케이션에 다 등록해주는 것이다.
이렇게 통합 테스트는 시간도 오래걸리고 모든 빈을 검사하기 떄문에 원치않은 것도 테스트할 수 있다. 그래서 자신이 원하는 빈만 등록을 하고 싶은 경우 사용하는 것이 Slice Test(슬라이스 테스트)이다.
이 슬라이스 테스트는 레이어별로 잘라서 적용이 되기 때문에 슬라이스 테스트인데, @JsonTest, @WebMvcTest, @WebFluxTest, @DataJpaTest 등등 다양한 테스트 애노테이션들이 있다. 그중에서 @WebMvcTest로 슬라이싱해서 Contorller 딱 하나만 테스트하는 방법을 알아보자.
@WebMvcTest 애노테이션은 MVC를 위한 테스트 애노테이션으로 클래스를 특정해서 테스트를 할 수 있다. 또한 Web layer만 빈으로 등록하기 때문에 가볍고 빠르게 테스트가 가능하다. 여기서 Web layer란 @Controller, @JsonComponent, Converter, GenericConverter, Filter, WebMvcConfigurer, HandlerMethodArgumentResolver이다. 일반적인 컴포넌트들은 빈으로 등록되지 않는다.
따라서, 모든 의존성이 끊기기 때문에 사용하는 의존성이 있다면 @MockBean으로 만들어서 채워줘야 한다.
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(SampleController.class)
class SampleControllerTest {
@MockBean
SampleService mockSampleService;
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void hello() throws Exception {
when(mockSampleService.getName()).thenReturn("gracenam");
mockMvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(content().string("hello gracenam"));
}
}
이런 식으로 작성을 하면, SampleController 하나만 빈으로 등록이 되기 때문에 훨씬 가벼운 테스트가 된다.
테스트 유틸리티
테스트가 제공하는 유틸리티가 4가지 정도 있다.
- OutputCapture
- TestPropertyValues
- TestRestTemplate
- ConfigFileApplicationContextInitializer
이 중에서 제일 유용할 법한 OutputCapture만 살펴보자.
OutputCapture는 Junit의 Rule3을 확장해서 만든 것이다. 로그를 비롯한 console에 찍히는 모든 것을 캡쳐하는 기능인데, 직접 코드를 작성해보자.
▶ SampleController.java
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class SampleController {
Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SampleController.class);
@Autowired
private SampleService sampleService;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
logger.info("nameunhye");
return "hello " + sampleService.getName();
}
}
▶ SampleControllerTest.java
package me.gracenam.springtestdemo.sample;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.boot.test.system.CapturedOutput;
import org.springframework.boot.test.system.OutputCaptureExtension;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import static org.mockito.Mockito.when;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.get;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.content;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(SampleController.class)
@ExtendWith(OutputCaptureExtension.class)
class SampleControllerTest {
@MockBean
SampleService mockSampleService;
@Autowired
MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void hello(CapturedOutput capturedOutput) throws Exception {
when(mockSampleService.getName()).thenReturn("gracenam");
mockMvc.perform(get("/hello"))
.andExpect(content().string("hello gracenam"));
assertThat(capturedOutput.toString()).contains("nameunhye");
}
}

Reference
Comments
SPRING BOOT 의 다른 글
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 데이터 4부 17 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 데이터 3부 16 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 데이터 2부 15 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 데이터 1부 14 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 11부 13 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 10부 10 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 9부 09 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 8부 08 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 7부 03 Sep 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 6부 05 Aug 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 5부 27 Jun 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 4부 13 Jun 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 3부 06 Jun 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 2부 05 Jun 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 스프링 웹 MVC 1부 30 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : Spring-Boot-Devtools 30 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 테스트 26 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 로깅 2부 25 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 로깅 1부 23 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 프로파일 23 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 외부 설정 2부 21 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : 외부 설정 1부 15 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 활용 : SpringApplication 11 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 원리 : 정리 06 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 원리 : 독립적으로 실행 가능한 JAR 06 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 원리 : 내장 웹 서버 04 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 원리 : 자동 설정 02 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 원리 : 의존성 01 May 2021
-
스프링 부트 시작하기 01 May 2021